Data fabric is a powerful architectural approach for integrating and managing data across diverse sources and platforms.
As enterprises navigate increasingly complex data environments, the need for seamless data access coupled with robust security has never been more critical. Data fabric has the potential to enhance both data security as well as governance, but it’s not always a straight path for organizations to achieve the optimal outcome.
Understanding data fabric architecture
To get the most of data fabric, it’s important to first actually understand what it is and what it can actually provide to an organization. Unfortunately, defining data fabric can also be a challenge.
[ Related: Data mesh vs. data fabric vs. data virtualization: There’s a difference ]
“Thanks to multiple, often vendor-centric, definitions, there remains confusion in the industry about the precise nature of data fabric,” Matt Aslett, director, with global technology research and advisory firm ISG, told InfoWorld.
ISG defines data fabric as a technology-driven approach to automating data management and data governance in a distributed architecture that includes on-premises, cloud and hybrid environments. Aslett added that a common misconception is that enterprises must discard existing data platforms and management products to embrace data fabric.
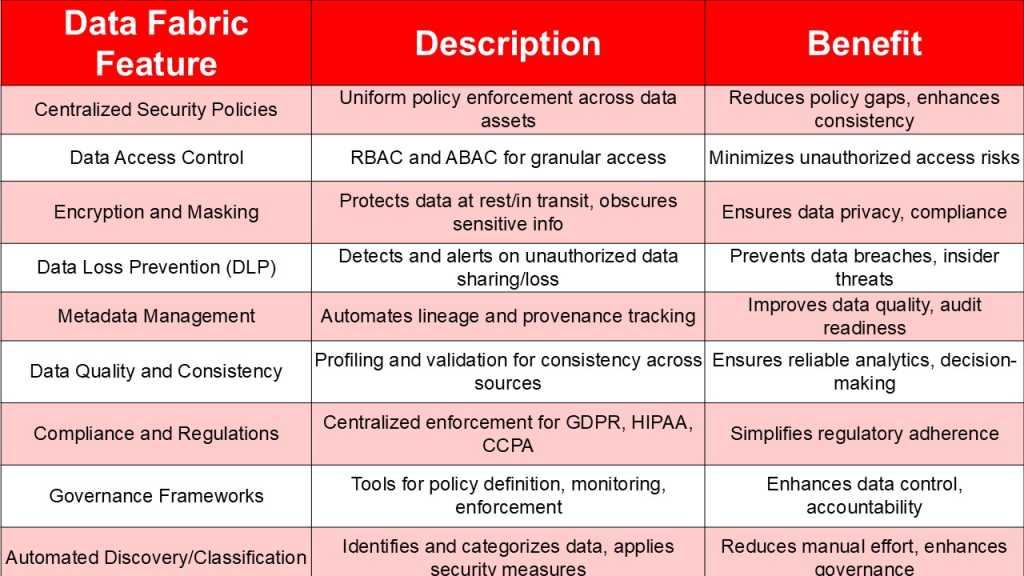
Quick answers on data fabric, security and governance
Key elements of a data fabric architecture include the following:
- Metadata-driven data identification and classification
- Knowledge graphs
- Automated, ML-driven, data management.
“These capabilities provide the connective tissue that traverses disparate data silos and can complement the use of existing bespoke data tools by facilitating an abstracted view of data from across the business to support business intelligence and artificial intelligence initiatives that rely on the data unification,” Aslett said.
Data security challenges
Implementing a data fabric architecture presents several security challenges that enterprisemust address to ensure the integrity, confidentiality and availability of data assets.
Among the security challenges are these six::
Data silos and fragmentation
Despite the promise of integration, many organizations struggle with persistent data silos in their initial data fabric implementations.
“The biggest challenge is fragmentation; most enterprises operate across multiple cloud environments, each with its own security model, making unified governance incredibly complex,” Dipankar Sengupta, CEO of Digital Engineering Services at Sutherland Global told InfoWorld.
Compliance and regulatory complexity
Adhering to industry standards and regulations such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (CCPA) is a significant challenge in data fabric implementations.
Different data types and sources may fall under different regulatory frameworks. As such, implementing consistent compliance measures across the entire fabric requires careful planning and execution.
Talent
According to Sengupta, the other blind spot is talent, with 82% of firms struggling to hire skilled data professionals.
Shadow IT
Shadow IT is also a persistent threat and challenge. According to Sengupta, some enterprises discover nearly 40% of their data exists outside governed environments. Proactively discovering and onboarding those data sources has become non-negotiable.
Data fragmentation
Another major obstacle to effective data security and governance is fragmentation.
“There are too many data silos to secure and govern, and too many tools required to get the job done,” Edward Calvesbert, Vice President, Product Management, for IBM watsonx.data, told InfoWorld.
IT complexity
According to Anil Inamdar, Global Head of Data Services at NetApp Instaclustr, the potential for data fabric security/governance challenges really begins with the complexity of the organization’s IT environment.
“If security is already inconsistent across hybrid or multi-cloud setups, teams will subsequently struggle to get their data fabric architecture as secure as it needs to be,” Inamdar said.
How data fabric enhances security
While there are some challenges, the reason why so many organizations choose to deploy data fabric is because it does significantly enhance data security and governance.
Data fabric architectures offer significant advantages for enhancing security when properly implemented across a number of different domains.
Centralized Security Policies
Organizations are using data fabric to fix the challenge of fragmentation. IBM’s Calvesbert noted that with data fabric organizations can create a centralized set of policies and rules capable of reaching all data within the organization. Policies and rules can be linked to any and all data assets through metadata like classifications, business terms, user groups, and roles – and then enforced automatically whenever data is accessed or moved.
Regulatory compliance
A data fabric deepens organizations’ understanding and control of their data and consumption patterns. “With this deeper understanding, organizations can easily detect sensitive data and workloads in potential violation of GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA and similar regulations,” Calvesbert commented. “With deeper control, organizations can then apply the necessary data governance and security measures in near real time to remain compliant.”
Metadata management
Automated metadata management and data cataloging are integral components and benefits of data fabric.
“It’s a big deal, because when metadata is automatically tagged and tracked across both cloud and on-prem environments, you are getting the level of visibility that is going to make security folks and compliance officers happy,” NetApp’s Inamdar commented. “Automating this process within a data fabric creates that digital breadcrumb trail that follows data wherever it goes.”
Automated data discovery and classification
Automated tools within data fabric discover and classify data, reducing manual effort and enhancing governance. This involves identifying sensitive data across environments, categorizing it and applying appropriate security measures.
Data access control and authorization
Data fabric supports granular access control through Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), ensuring only authorized users can access sensitive data. This is vital for minimizing unauthorized access risks, with mechanisms like dynamic masking complementing these controls.
Data encryption and masking
Data fabric facilitates data encryption for protection at rest and in transit and data masking to obscure sensitive information. Encryption transforms data so it’s not transparent and available for anyone to look at, while masking replaces data with realistic but fake values, ensuring privacy.
Data governance frameworks
Data fabric supports implementing and enforcing data governance frameworks, providing tools for policy definition, monitoring, and enforcement. This ensures data is managed according to organizational policies, enhancing control and accountability.
IDG
Why data validation is critical for data fabric success
Data security and governance inside a data fabric shouldn’t just be about controlling access to data, it should also come with some form of data validation.
The cliched saying “garbage-in, garbage-out” is all too true when it comes to data. After all, what’s the point of ensuring security and governance on data that isn’t valid in the first place?
“Validating the quality and consistency of data is essential to establishing trust and encouraging data usage for both BI and AI projects,” Alslett said.
So how can and should enterprises use data validation within a data fabric? Sutherland Global’s Sengupta commented that the most effective validation strategies he has seen start with pushing checks as close to the source as possible. He noted that validating data upfront —rather than downstream — has helped reduce error propagation by over 50% in large-scale implementations. This distributed approach improves accuracy and lightens the processing load later in the pipeline.
Machine learning is playing a growing role as well. Statistical baselines and anomaly detection models can flag issues that rigid rule-based systems often miss. In one case cited by Sengupta this approach helped increase trust in critical data assets by nearly 80%.
“What’s often overlooked, though, is the value of context-aware validation—cross-domain consistency checks can expose subtle misalignments that may look fine in isolation,” Sengupta said. “For real-time use cases, stream validation ensures time-sensitive data is assessed in-flight, with accuracy rates approaching 99.8%.”
Benefits and use cases: data fabric in the real world
The real world impact of data fabric is impressive. While it can often just be used as a marketing term by vendors, there is tangible return on investment opportunities too.
“In our work with large enterprises, the most tangible impact of data fabric initiatives comes from their ability to speed up access to trustworthy data, safely and at scale,” Sengupta said.
For instance, a global financial institution reduced its regulatory reporting time by 78% and accelerated access provisioning by 60% after re-architecting its data governance model around unified security policies.
In healthcare, a provider network improved patient data accuracy from 87% to 99%, while also cutting integration time for new data sources by 45%, a critical gain when onboarding new partners or navigating compliance audits.
A manufacturing client saw a 52% drop in supply chain data errors and significantly improved the processing of IoT sensor data, boosting integration speed by 68%.
In retail, better orchestration of policies and quality controls translated into 85% faster delivery of customer insights, a 3x increase in analyst productivity, and a 30% reduction in storage costs through better data hygiene.
“What these outcomes show is that when data is treated not just as an infrastructure component but as an enabler of business velocity, the returns are both measurable and strategic,” Sengupta said.
Source:: Network World
